The year 2024 stands as a landmark in the financial services landscape, marked in part by an expectation of continued growth in neobanking. Referring to a new breed of financial institution, these digital-first organizations are redefining the traditional banking model, catering to the modern demands for rapid, efficient, and personalized financial services by operating solely in the digital space.
The origin of neobanks can be traced back to between 2013 and 2015, with some of the first players – initially termed as “‘challenger banks,” starting up in the UK and Germany. Companies such as Monzo, Revolut, N26, and Atom Bank were among the pioneers in this sector. The term “neobanking” itself was first coined in 2017 to describe tech-based financial service providers that were challenging traditional banks.
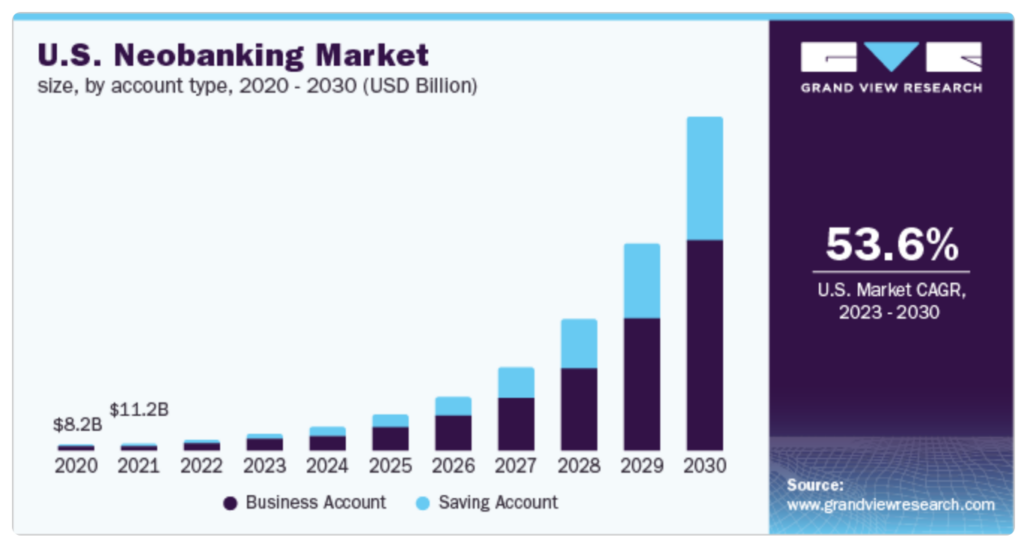
Reflecting a major shift in the market, the global neobanking sector, which was valued at USD 66.82 billion in 2022, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 54.8% from 2023 to 2030. This forecast, as reported by Grandview Research, highlights the sector’s upward trajectory and its growing appeal among consumers and enterprises alike.
The remarkable rise of neobanking is not solely a result of shifting consumer preferences but is also a testament to the sector’s continuous technological innovation. And the momentum looks to continue: as noted in a report by the Financial Brand, the total may actually double by 2025. As neobanks navigate the terrain of 2024, they face the dual challenge of maintaining their innovation-driven momentum while adapting to an evolving regulatory landscape. The focus now shifts to the technological advancements that are at the forefront of driving this banking revolution forward.
Technological Innovations Driving Neobanking
The unprecedented rise in neobanking is largely fueled by cutting-edge technological advancements. Beyond the buzzwords of blockchain and artificial intelligence – though these, too, are driving the sector – neobanks are drawing on today’s full range of innovative technologies to redefine banking experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. AI and machine learning stand at the core of neobanking’s evolution, enabling personalized banking experiences. Recent insights from Tillo highlight the use of AI algorithms in analyzing customer spending patterns and offering tailored budgeting advice. This level of personalization is transforming customer perceptions, setting neobanks apart from traditional banking systems.
- Digital and Mobile-First Banking. The shift toward a mobile-first approach in banking is significant. With customers increasingly managing finances on-the-go, neobanks are offering comprehensive mobile banking solutions, characterized by intuitive user interfaces and seamless integration with other financial services.
- Big Data and Analytics. Neobanks are harnessing the power of big data, combined with machine learning, to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, risk assessment, and market trends. This data-driven approach aids in tailoring products and services to meet specific customer needs, thereby enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
- Cloud Computing and API Integration. The embrace of cloud computing allows neobanks to operate with greater agility and scalability. API (Application Programming Interface) integration further facilitates the collaboration between financial services, fintech startups, and traditional banks, leading to an ecosystem that is more interconnected and innovative.
- Cybersecurity and Data Protection. As all banking fundamentally involves proper handling of sensitive financial data, neobanks are investing heavily in robust cybersecurity measures. Advanced encryption techniques, secure APIs, and constant monitoring systems are being deployed to safeguard against cyber threats and ensure data privacy.
- Blockchain Beyond Buzzwords. While blockchain’s hype can overstate its influence at times, its practical applications in neobanking are substantial. It’s not just about cryptocurrencies; blockchain technology provides a secure, transparent framework for transactions, enhancing trust and efficiency in digital banking operations.
These technological underpinnings not only enable neobanks to offer superior services but also lay the foundation for future advancements in the financial sector. As neobanks continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in digital banking, they set new standards for customer experience and operational efficiency in the financial world.
Neobanks vs. Traditional Banks: A Comparative Analysis
The ascent of neobanks has brought them into direct competition with traditional banks, marking a shift in how financial services are consumed and provided. This contrast is stark in several key areas:
- Technological Agility. Neobanks, born in the digital age, inherently possess a technological edge. Their infrastructure is built ground-up with digital technology, enabling rapid adaptation to changing market needs and consumer behavior. In contrast, traditional banks often grapple with legacy systems, making their transition to digital-first solutions more cumbersome. Neobanks like Monzo have pioneered features such as fraud call checkers, setting a benchmark for legacy banks to follow, according to FinTech Magazine.
- Customer Experience and Services. The neobanking model prioritizes customer experience (CX), offering products designed with user convenience and personalization at their core. This approach contrasts with the more traditional, one-size-fits-all product suite of legacy banks. Oriana Ascanio from Foundever notes the importance of banks focusing on customer service propositions, aligning policies, processes, and systems with customer expectations.
- Market Reach and Customer Preferences. While traditional banks have long-established customer bases and extensive nextworks of physical branches, neobanks are rapidly gaining ground, especially among digitally-savvy consumers. Their ability to offer services remotely aligns well with the lifestyle of modern consumers who prefer managing their finances online.
- Innovation and Product Development: Neobanks are often quicker to market with new products due to a leaner operational model. They can experiment and iterate more quickly, which offers a flexibility not always present in the more risk-averse and regulated environment of traditional banks.
- Regulatory Compliance and Trust: While neobanks face the dual challenges of building trust and navigating regulatory frameworks, traditional banks benefit from established reputations and compliance structures. However, as neobanks mature and gain credibility, this gap is narrowing.
The landscape in 2024 suggests a coexistence where neobanks and traditional banks learn from each other. While neobanks are pushing the boundaries of innovation and customer experience, traditional banks are leveraging their scale and trust to adapt to the digital era. The competition between these two models is ultimately driving the entire financial industry towards greater efficiency, innovation, and customer-centricity.
Challenges and Regulatory Landscape for Neobanks in 2024
As neobanks continue their upward trajectory, they face a complex array of challenges and a dynamic regulatory landscape that shapes their operations and strategies.
- Scalability and Technological Challenges. One of the primary challenges still looming before neobanks is finding a way to scale their technology infrastructure to support rapid growth. This involves not just expanding their customer base but also ensuring that their platforms remain robust, secure, and capable of handling increased transaction volumes without compromising on speed or user experience.
- Security and Data Privacy. In the digital banking space, cybersecurity remains a paramount concern. Neobanks, handling sensitive financial data, must employ advanced security measures to protect against cyberthreats and data breaches. It’s an ongoing to challenge to ensure customer data privacy and compliance with global data protection regulations, and that requires constant vigilance and innovation in security protocols.
- Regulatory Compliance. Navigating the regulatory landscape is a complex task for neobanks. Different regions have varying regulatory requirements, and keeping up with these changes, especially for neobanks operating across multiple jurisdictions, is critical. Ensuring compliance with financial regulations, anti-money laundering (AML) standards, and know-your-customer (KYC) protocols is essential for maintaining operational legitimacy and customer trust.
- Building Trust and Customer Confidence. For many consumers, especially those accustomed to traditional banking, trusting a fully digital bank with their finances is a significant leap. Neobanks need to continuously build customer confidence, not only through reliable and secure services but also by demonstrating financial stability and long-term viability.
- Competition from Traditional Banks and Fintechs. As traditional banks enhance their digital offerings and fintechs introduce innovative financial products, the competition for neobanks intensifies. Standing out in this crowded market requires a combination of innovative products, superior customer experience, and effective brand communication.
Despite these challenges, the opportunity landscape for neobanks is vast. As they refine their business models and adapt to these challenges, neobanks are poised to redefine the future of banking. Their ability to innovate, respond to customer needs, and navigate the complex regulatory environment will be key to their continued success and influence in the global financial ecosystem.
Future Outlook
As 2024 unfolds, the future of neobanking appears increasingly influential in shaping the global financial landscape. The trajectory of neobanking is not just defined by its current success but also by its potential to continuously innovate and adapt to changing market dynamics and customer needs.
- Innovation and Customer-Centric Products. The future will likely see neobanks further leveraging technologies like AI, blockchain, and cloud computing to offer more personalized and secure banking experiences. The focus will be on developing products that are not only technologically advanced but also deeply aligned with customer lifestyle and financial goals.
- Expansion and Global Reach. Neobanks are poised to expand their global footprint, entering new markets and catering to a diverse customer base. This expansion will be facilitated by the inherently scalable digital model of neobanks, coupled with strategic partnerships and regulatory compliance across different regions.
- Competition and Collaboration. As the competition with traditional banks intensifies, there will also be increased opportunities for collaboration. Partnerships between neobanks and traditional financial institutions may become more common, combining the agility of neobanks with the scale and trust of established banks.
- Regulatory Evolution. The regulatory environment will continue to evolve, with a potential shift towards more standardized regulations for digital banking. This evolution will play a crucial role in shaping the operations and growth strategies of neobanks.
- Financial Inclusion and Social Impact. One of the most significant impacts of neobanking will be its role in advancing financial inclusion. By offering accessible and affordable banking services, neobanks have the potential to reach underserved and unbanked populations, making a considerable social impact.
- The Road to Profitable Growth. As neobanks navigate the evolving financial landscape, a key focus lies in unlocking paths to profitable growth. Insights from Simon-Kucher suggest that this can be achieved through a blend of strategic pricing, innovative product development, and enhanced customer engagement. By fine-tuning their pricing models, neobanks can optimize revenue streams while ensuring customer satisfaction.
Additionally, embracing product innovation allows these institutions to cater to niche market segments and specific consumer needs, thereby differentiating themselves in a crowded marketplace. Furthermore, prioritizing customer engagement and experience is crucial for building brand loyalty and trust, which are essential for sustainable growth. This multifaceted approach positions neobanks not just to survive but to thrive in the competitive financial sector.
As we look ahead, neobanking stands as a beacon of innovation, customer-centricity, and financial democratization. Its journey is a testament to the transformative power of technology in the financial sector, and its continued evolution will undoubtedly influence the way we think about and interact with banking services.
For a complete list of digital banks worldwide, see The Financial Brand’s Digital Bank Tracker.
– Jessica Purdy